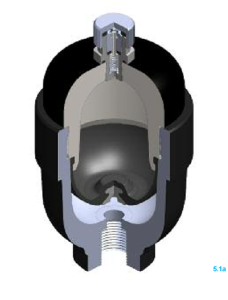
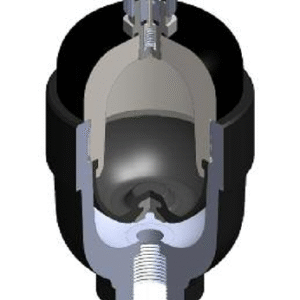
How Does a Diaphragm Accumulator Work
The diaphragm accumulator’s working principle is based on the functioning of its mechanically sealed, strong yet flexible diaphragm. The accumulator comprises a shell that withstands the internal pressure, a diaphragm, a gas valve, and a fluid port which connects to the hydraulic circuit. Inside a pressure-resistant shell, the flexible diaphragm separates a pre-charged gas, usually nitrogen, from the hydraulic fluid. When hydraulic pressure rises, the fluid pushes against the diaphragm, compressing the gas. When pressure drops, the gas expands, forcing the fluid back into the system to maintain balance. Pre-charge pressure plays a key role in performance. Setting it correctly ensures smooth operation, consistent pressure control, and longer diaphragm life.
Key Features and Benefits of Diaphragm Accumulators
- Diaphragm accumulators are a smart choice for hydraulic systems requiring stable pressure and reliable energy storage. They offer several practical advantages across industries. Here are some of the benefits.
- Flexible diaphragm: The flexible diaphragm reacts instantly to pressure changes, making it ideal for systems with frequent load variations. It also separates gas and fluid, which makes these accumulators resistant to fluid contamination.
- Optimal hydraulic system performance: They offer high efficiency in energy storage and pressure stabilization. Minimal internal friction ensures maximum energy storage and quick release.
- No moving parts: Simple construction without moving parts makes these accumulators low on maintenance. They enable quick inspection and diaphragm replacement when needed.
- Compact design: These are space-saving and lightweight than most other accumulators, making them suitable for installations in constrained spaces.
- Long service life: The diaphragm hydraulic accumulators in our selection are made from materials and precise engineering. This offers consistency, reliability, and a long operational time.
- Wide fluid compatibility: These accumulators work with a range of hydraulic fluids including mineral oils and synthetic types.
Common Applications of Diaphragm Accumulators
Diaphragm type accumulators are used in many hydraulic systems where performance, reliability, and compact size are critical. Our diaphragm hydraulic accumulators help protect components, improve response time, and reduce overall system wear. Here are some typical applications.
- Construction and earth-moving machinery: In heavy equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and cranes, hydraulic systems experience constant changes in pressure and load. A diaphragm accumulator acts as a pressure stabilizer and shock absorber, ensuring the hydraulic fluid pressure remains steady during sudden load shifts. Our accumulators are designed to withstand dust, vibration, and temperature extremes.
- Industrial hydraulics and presses: Industrial presses, machine tools, and forming systems rely on hydraulic energy for controlled motion and consistent pressure delivery. In these applications, a diaphragm hydraulic accumulator serves different purposes. These include storing hydraulic energy for short, high-demand operations, compensating for small leaks and temperature-related volume changes, reducing pulsation from pumps.
- Mobile and agricultural equipment: These accumulators offer energy storage and reduce system vibration in compact designs. They find application in various mobile and agricultural hydraulic systems such as tractors, harvesters, forklifts, and utility vehicles. These accumulators help in damping vibrations generated by uneven terrain or machine motion. They supply hydraulic energy during pump shutdowns or engine idling.
- Oil & gas: These accumulators are applicable in onshore and offshore oilfield operation as they ensures stable pressure control in environments with varying loads and temperatures. They act as vital pressure buffers and energy reserves in these environments, and absorb pressure surges. Also, they maintain consistent hydraulic power for subsea actuators.
- Marine: Marine hydraulic systems used in steering, stabilizing, and deck machinery require constant and reliable pressure control. A diaphragm type accumulator provides the cushioning effect necessary to counteract wave-induced pressure variations and vibration. They also ensure immediate hydraulic response when rudder control is engaged. Our compact, corrosion-resistant diaphragm accumulators are suited for salt water environments.
- Defense: Hydraulic systems in defense vehicles, aircraft, and naval equipment depend on consistent pressure and rapid response. Diaphragm accumulators are used for storing energy for emergency actuation systems, damping shock and vibration from weapon discharge or rapid motion, and maintaining steady pressure in mission-critical control circuits.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Diaphragm Accumulator
Choosing the right diaphragm accumulator requires considering several key factors. Here are some of them.
- Pressure requirements: Identify the highest system pressure, keeping a decent margin. Check the pressure ratio between the maximum and minimum values, as it directly impacts the efficiency. Check the capacity and pre-charge pressure as it determines the accumulator’s energy storage and responsiveness.
- Volume and capacity: Calculate the fluid volume based on your application requirements, such as energy storage, pulsation dampening, and so on. For correct sizing of the accumulator, use proper sizing formulas that account for gas laws and compression ratios.
- Fluid compatibility: Check the chemical composition of hydraulic fluid or process medium to ensure the diaphragm and seals resist chemical degradation. Also, check the proportion of additives and contaminants in the fluid.
- Mounting and accessibility: These aspects directly impact the ease of maintenance and the safety of installation. Evaluate the available installation space, preferred orientation, and maintenance accessibility when selecting mounting options. Additionally, ensure that service technicians can access gas valves and replacement components during scheduled maintenance intervals.
- Quality Standards: Verify if the accumulator has undergone through testing and inspection. As part of the process, each hydraulic diaphragm accumulator is subjected to rigorous vibration and pressure testing. They also undergo dimensional inspection and leak verification. Precision-machined components and certified materials ensure reliable performance and a long operational life, meeting ASME and ISO standards.
- Customization: You can choose customized diaphragm accumulators to meet specific requirements, including non-standard volumes, pressure ratings, port configurations, special materials, or unique mounting arrangements. Technical support is available for sizing calculations and application analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should a diaphragm accumulator be recharged
Ans. Typically, every 6–12 months, depending on usage and system conditions. Checking pre-charge pressure during routine maintenance helps prevent failures.
2. What are the signs of diaphragm failure?
Ans. Reduced pressure stability, fluid leakage, or gas discharge into the hydraulic line are common indicators.
3. What gas is used inside a diaphragm accumulator?
Ans. Nitrogen is used because it is inert, stable, and safe under pressure.